Introduction
Table of Contents
Brief Overview of Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1 and Type 2)
Diabetes Mellitus refers to a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood sugar (glucose) levels over a prolonged period. There are two main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It typically develops in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy to regulate blood sugar levels. Tackling the challenges of Type 1 diabetes involves understanding the need for continuous insulin management and monitoring.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is the most common form of diabetes, typically occurring in adults but increasingly affecting children and adolescents. In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough, leading to high blood sugar levels. It can often be managed with lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, although medication or insulin may eventually be required. Tackling the challenges of Type 2 diabetes involves adopting healthier habits and closely monitoring blood glucose levels to avoid complications.

The Global Prevalence and Its Impact on Health
Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health is a global priority, as millions of people are affected by this condition worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 400 million people are living with diabetes globally, and this number is expected to rise significantly due to increasing rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and aging populations.
- Prevalence: Type 2 diabetes accounts for approximately 90-95% of all diabetes cases, while Type 1 diabetes makes up the remainder. As the global prevalence increases, tackling the challenges of diabetes becomes more critical for both individuals and healthcare systems.
- Health Impact: Diabetes is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. It increases the risk of developing serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, and nerve damage. Tackling the challenges of diabetes is essential to preventing these life-altering complications and ensuring better health outcomes for individuals.
Why Addressing the Challenges of Diabetes Mellitus is Essential for Better Health Outcomes
Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health is not only about improving individual well-being but also about reducing the global healthcare burden. Addressing these challenges is critical to improving the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes and minimizing long-term complications.
- Prevention of Complications: Effective diabetes management can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and amputations. By tackling the challenges of diabetes through early intervention, regular monitoring, and lifestyle changes, individuals can prevent these outcomes.
- Improved Quality of Life: Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying active can help people with diabetes feel better physically and emotionally. Tackling the challenges of diabetes empowers individuals to lead more fulfilling lives by reducing the psychological and physical burden of the disease.
- Healthcare System Strain: Diabetes-related complications lead to increased healthcare costs, hospitalizations, and long-term care. By tackling the challenges of diabetes early on, we can reduce the overall burden on healthcare systems and improve public health outcomes.
Common Challenges Faced by People with Diabetes
- Blood Sugar Control – Managing blood sugar levels is one of the biggest challenges for people with diabetes. Blood sugar can fluctuate throughout the day, making it difficult to maintain a steady level. Tackling the Challenges: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is key to staying on track. Using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can help people stay aware of their levels. Also, adopting a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress are crucial to keeping blood sugar stable. By tackling the challenges of diabetes, individuals can improve their control and avoid dangerous spikes or drops in glucose.
- Dietary Restrictions – Food plays a significant role in managing diabetes, but the restrictions can feel overwhelming at times. From counting carbs to avoiding sugary snacks, it can be difficult to figure out what to eat. Tackling the Challenges: The key is finding a healthy, sustainable eating pattern that works for you. Focus on a variety of whole foods, including vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Instead of thinking of food as a restriction, think of it as a way to fuel your body and maintain energy levels. Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health means creating a balanced approach to food that doesn’t leave you feeling deprived.
- Emotional and Mental Health struggles – Living with diabetes can sometimes lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or even depression. Constantly managing the condition can feel overwhelming, and many people experience diabetes burnout at some point. Tackling the Challenges: Taking care of your mental health is just as important as physical health. Support groups, therapy, and mindfulness practices like meditation can be valuable tools. Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health includes seeking emotional support, staying positive, and remembering that you don’t have to go through it alone.
Risk of Long term complications
Taking care of one’s health, especially when dealing with a lifestyle disease, is crucial for preventing long-term risks and complications. In the case of diabetes, if it is not properly managed, it can lead to serious or chronic complications, making it difficult to lead a comfortable life. Let’s see what are the major long term complications!
- Diabetic Retinopathy – Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a common complication of diabetes mellitus, characterized by damage to the retinal blood vessels, which can lead to vision impairment and blindness if not properly managed. It is a leading cause of visual loss among adults worldwide
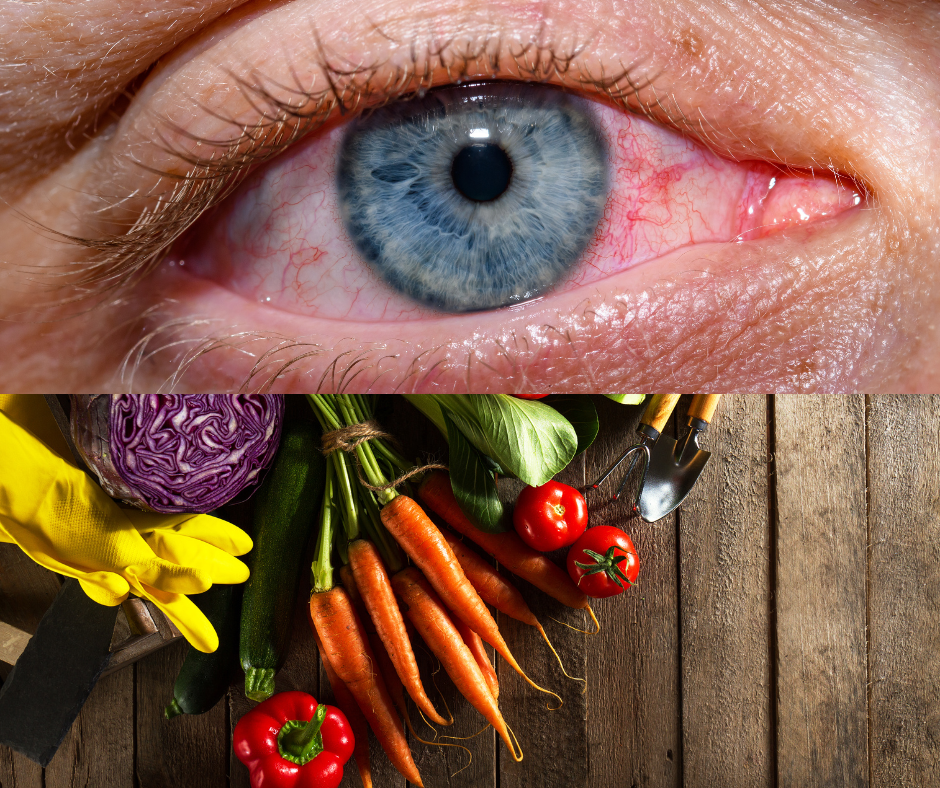

Nutritional Management – Protective Dietary Factors:
Mediterranean Diet: Adherence to a Mediterranean diet, characterized by high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil, along with moderate fish intake, has shown a protective effect against DR. The diet’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant components may contribute to this benefit. MDPI
Fruits, Vegetables, and Dietary Fiber: High consumption of fruits, vegetables, and dietary fibers has been associated with a reduced risk of DR. These foods are rich in antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory properties that may protect retinal health. MDPI
Fish and Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Regular intake of fish, particularly oily fish rich in long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCω3PUFAs), has been linked to a lower risk of DR. These fatty acids possess anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties beneficial for retinal health. MDPI
2. Heart diseases – Diabetes mellitus (DM) significantly elevates the risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), including coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, and heart failure. This increased risk is attributed to factors such as hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and associated conditions like hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Dietary recommendations –
1. Mediterranean Diet: Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil, this diet is rich in monounsaturated fats (MUFAs) and has been shown to improve metabolic risk factors in patients with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and CVD.
2. DASH Diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet focuses on reducing sodium intake and increasing consumption of nutrient-rich foods. It has been effective in lowering blood pressure and improving lipid profiles, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes and heart disease.
3. Increased Intake of MUFAs: Diets high in monounsaturated fats, such as those found in olive oil and nuts, can favorably influence plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations, reducing the risk of coronary heart disease events in both non-diabetic and diabetic individuals.
4. Nutrient-Rich Foods: Consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, non-starchy vegetables, nuts, legumes, fish, vegetable oils, and yogurt, is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes
Nutrition Tips for managing Diabetes
When it comes to Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health, nutrition plays a huge role in managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and preventing complications. Let’s dive into the key aspects of diabetes-friendly eating, backed by research, to help you take control of your health!
- Emphasizing the Role of a Balanced Diet: High Fiber, Healthy Fats, and Lean Proteins – A balanced diet is crucial for managing diabetes. High fiber foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins help maintain stable blood sugar levels and provide lasting energy.
How It Helps:
- High fiber: Helps slow down the absorption of sugar, preventing spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Healthy fats: Found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, these fats can improve heart health, which is crucial since people with diabetes are at a higher risk for cardiovascular disease.
- Lean proteins: Skinless poultry, fish, and plant-based proteins (like beans) are excellent choices that help keep you full without affecting blood sugar levels.
2. Foods to Include and Avoid: The Power of Low Glycemic Index Foods
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar. Foods with a low GI cause a slower, more gradual increase in blood sugar, making them ideal for diabetes management.
Foods to Include:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, and barley are great low-GI choices that provide fiber and nutrients.
- Non-starchy vegetables: Leafy greens, tomatoes, and peppers are low-GI, nutrient-packed foods that help regulate blood sugar.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas have a low glycemic index and are rich in fiber and protein.
Foods to Avoid:
- Refined carbs: White bread, white rice, and sugary cereals are high-GI and can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
- Processed snacks: Chips, cookies, and sugary drinks are high in unhealthy fats and sugars, which can make blood sugar management harder.
Exercise: A Key Factor in Diabetes Control
- The Benefits of Regular Physical Activity on Insulin Sensitivity – When you exercise, your body uses insulin more efficiently, which means your cells become better at absorbing glucose (sugar) from your bloodstream. This helps keep blood sugar levels in check and improves overall insulin sensitivity.
How It Helps:
- Increased insulin sensitivity means that your body requires less insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. By doing regular exercise, insulin sensitivity can also be taken care of!
- Lower blood sugar levels: Physical activity helps move glucose into your cells, lowering blood sugar and reducing the risk of spikes.
- Improved heart health: Regular exercise strengthens the heart and helps prevent cardiovascular complications, which people with diabetes are at a higher risk for.
2. Types of Exercise That Are Particularly Effective for People with Diabetes
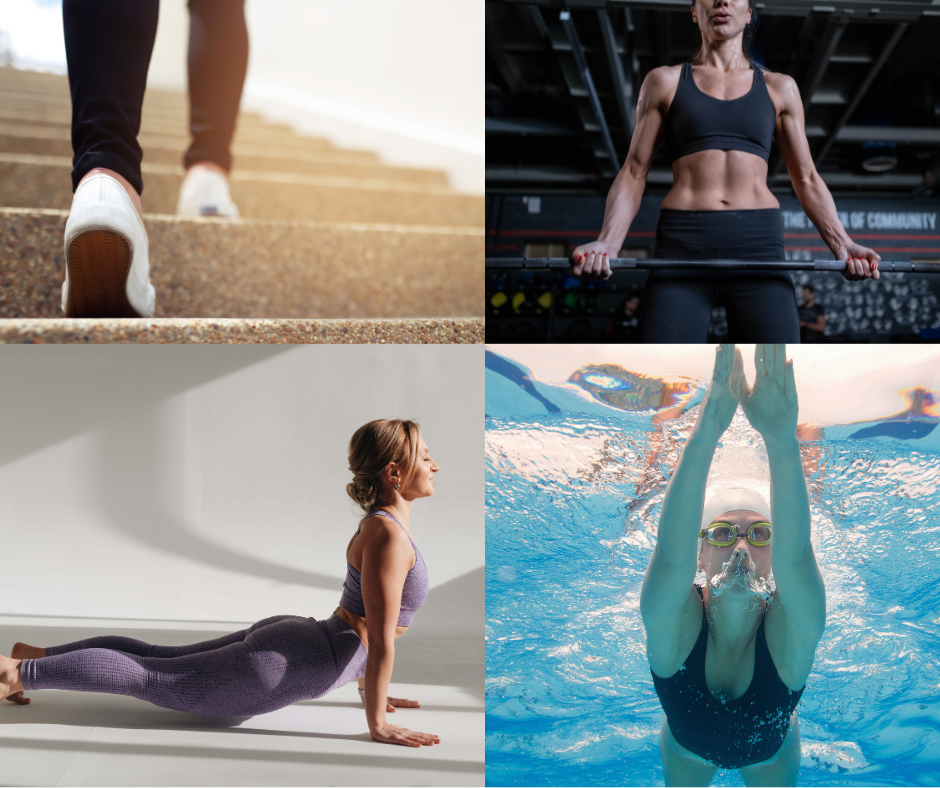

Different types of exercise offer unique benefits for people with diabetes. Here are some of the most effective options for managing Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health:
Walking:
- One of the simplest and most effective forms of exercise, walking helps improve cardiovascular health and regulate blood sugar levels. It’s also low-impact, making it ideal for people of all fitness levels.
- Pro Tip: Try a 10 – 20 minute walk after meals to help manage blood sugar spikes!
Strength Training:
- Lifting weights or using resistance bands helps build muscle mass, which in turn helps the body use insulin more efficiently. For those with Diabetes Mellitus , strength training is an essential component of exercise routines to improve glucose control and overall health.
- Pro Tip: Start with light weights or bodyweight exercises like squats, lunges, or push-ups. Gradually increase intensity as you get stronger.
Aerobic Exercise:
- Activities like walking, cycling, and swimming help improve cardiovascular health, which is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Aerobic exercises can enhance insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health often includes these activities as a foundation for long-term management.
- Pro Tip: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as 30 minutes of cycling five days a week.
Low-Impact Exercise:
For individuals with joint pain or other mobility issues, low-impact exercises like water aerobics or cycling can be an effective way to stay active without putting excessive strain on the body. This approach is often recommended in Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health to ensure safe and sustainable activity.
3. How to Stay Motivated and Create an Exercise Routine
Staying motivated can be tough, but creating a sustainable exercise routine that fits into your life is key to success. Here are some tips to help you stick with it!
Set Realistic Goals: Start small and gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts. Celebrate your progress along the way!
Track Your Progress: Keep a fitness journal or use an app to track your workouts and improvements in blood sugar control. This will help you see how far you’ve come.
Find Activities You Enjoy: If you love dancing, take a dance class! If you enjoy being outdoors, try hiking or cycling. Finding an activity you look forward to will make sticking with it easier.
Buddy Up: Find a workout buddy to keep you accountable. Exercising with a friend or family member can make it more fun and motivate you to stay consistent.
Reward Yourself: Celebrate your achievements with non-food rewards like a new workout outfit, a relaxing massage, or a fun activity.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Success
Managing diabetes isn’t a one-time effort—it’s about making small, sustainable changes that lead to long-term success. Let’s talk about the power of consistency and the importance of creating a supportive environment that helps you thrive.
- The Importance of Consistency and Gradual Changes in Lifestyle
When it comes to managing Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health, consistency is key. Trying to make big changes all at once can be overwhelming and hard to stick with. But by focusing on small, gradual improvements, you’ll be more likely to maintain a healthy lifestyle over time.
Why It Matters:
- Small Steps Lead to Big Results: Instead of trying to overhaul your entire lifestyle overnight, focus on making one small change at a time. Whether it’s eating more vegetables, going for a daily walk, or getting better sleep, each little step counts.
- Consistency is Key: Consistent habits, like checking your blood sugar, eating balanced meals, and staying active, will have a more lasting impact than occasional efforts. Over time, these habits become part of your routine, making them easier to maintain.
How to Stay Consistent:
- Set Realistic Goals: Start with small, achievable goals that fit your lifestyle. For example, if you’re new to exercise, aim for a 10-minute walk each day and gradually increase the time.
- Celebrate Progress: Acknowledge your efforts, no matter how small. Every healthy choice is a step in the right direction, so celebrate the wins!
- Create a Routine: Building a daily or weekly routine around your meals, exercise, and diabetes management can make it easier to stay on track. Having a set time for these activities makes them feel like a normal part of your day.
2. Building a Supportive Environment: Family, Friends, and Online Communities
Managing diabetes is easier when you have a strong support system in place. Whether it’s family, friends, or online communities, having people around you who understand your goals and challenges can make all the difference. In the context of Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health, a supportive network can provide encouragement, help with decision-making, and offer practical assistance, making it easier to stay on track with lifestyle changes, medication management, and emotional well-being. Having a strong support system is key to overcoming the daily hurdles that come with managing diabetes.
Why It Matters:
- Encouragement and Accountability: A supportive environment can motivate you to stick with your healthy habits. Family and friends can encourage you, cheer you on, and hold you accountable.
- Shared Experiences: Sometimes, it’s helpful to talk to people who are going through the same thing. They understand the struggles and can offer advice, empathy, or simply a listening ear.
How to Build Your Support System:
- Talk to Your Family and Friends: Let them know how they can support you in your journey. Whether it’s cooking healthy meals together, joining you for exercise, or just offering words of encouragement, their support can make a huge difference.
- Join an Online Community: Online forums, social media groups, and apps can connect you with others who have diabetes. Sharing tips, experiences, and even challenges with people who understand can be incredibly empowering.
- Find a Buddy: Having an exercise buddy or someone to share healthy recipes with can keep you motivated. It’s more fun to work on your goals with someone else by your side!
Conclusion
Managing Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health isn’t just about managing blood sugar levels—it’s about taking a proactive approach to your overall well-being. When you embrace healthy habits, stay motivated, and focus on the bigger picture, you’re not only controlling your diabetes, but you’re also enhancing your quality of life.
Living with diabetes is a journey, and while there are challenges, there are also countless opportunities for empowerment. By adopting a proactive approach, staying consistent, and focusing on your overall health, you can tackle the challenges of diabetes and live your best life.
Remember, Diabetes Mellitus: Tackling the Challenges for Better Health is about making small, positive changes that add up over time. Stay motivated, be kind to yourself, and celebrate every step forward—you’ve got this!
For more such nutrition information click here
